How To Calculate Long Run Marginal Cost
How To Calculate Long Run Marginal Cost. Long run marginal cost curves: Market demand equals market supply, qd(p*) = q* = qs(p*),
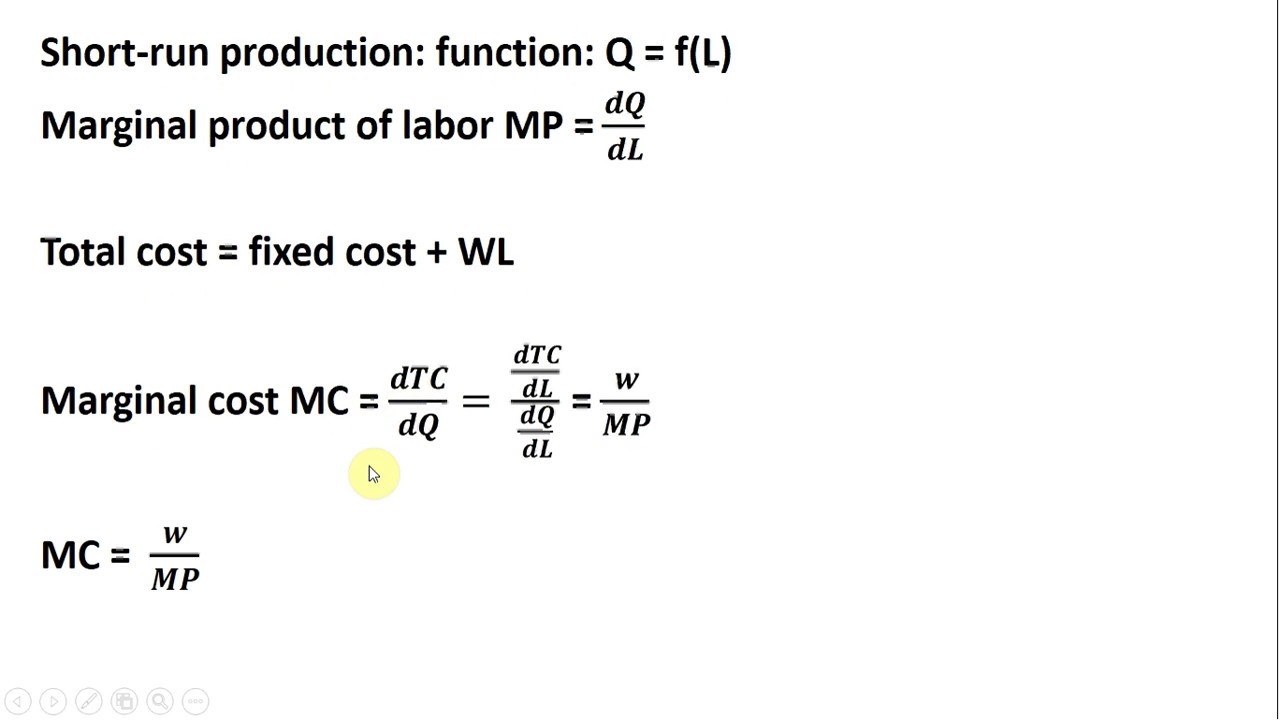
Mc = δ tc/ δ q. The long run marginal cost measures the cost to produce a unit of electric energy where we don't assume that the capacity of the plant is fixed. For example, suppose the total cost of producing 1,000 widgets is $4,500.
Current Methods Of Calculating Long Run Marginal Cost Lrmc Can Be Calculated And Applied In Various Ways.
It has been obtained by joining together points indicating 2/3rd utilization of production capacity of different short run average cost curves. Marginal cost = change in total cost / change in quantity. Determine the optimal combination of resources given a set of constraints that can satisfy the forecasted demand.
In Principle, Prices Could Reflect Either Srmc Or Lrmc.
The formula used to calculate marginal cost is: Marginal cost = change in costs / change in quantity marginal cost represents the incremental costs incurred when producing additional units of a good or service. Marginal cost = change in total cost/ change in output.
Calculate The Lrmc By Dividing The Present Value Of The Optimal
If the firm plans to produce in the long run at an output of q 3 , it should make the set of investments that will lead it to locate on srac 3 , which allows producing q 3 at the lowest cost. Long run equilibrium a long run equilibrium is a price p*, quantity q* and number of firms n, such that: Lrtc= ∆ lrtc /∆q it, therefore, measures the change in total cost per unit of output as the firm moves along the long run total cost curve (or the expansion path).
You May See The Formula Transcribed Using Mathematical Symbols, Like This:
25 lac has been shown. Market demand equals market supply, qd(p*) = q* = qs(p*), The production process for typing works best with one worker and one pc.
Mathematical Concept Of Lrmc Dlrc Dd
Lrmc = lrc function represents the total cost function of the optimal expansion path which can be achieved by simultaneous adjusting of all inputs. Firms must be making zero profits so that p*=ac(q*) 3. Marginal cost calculator this marginal cost calculator allows you to calculate the additional cost of producing more units using the formula:
